Toy Factory Simulation Using core.async (3)
Assembly Line
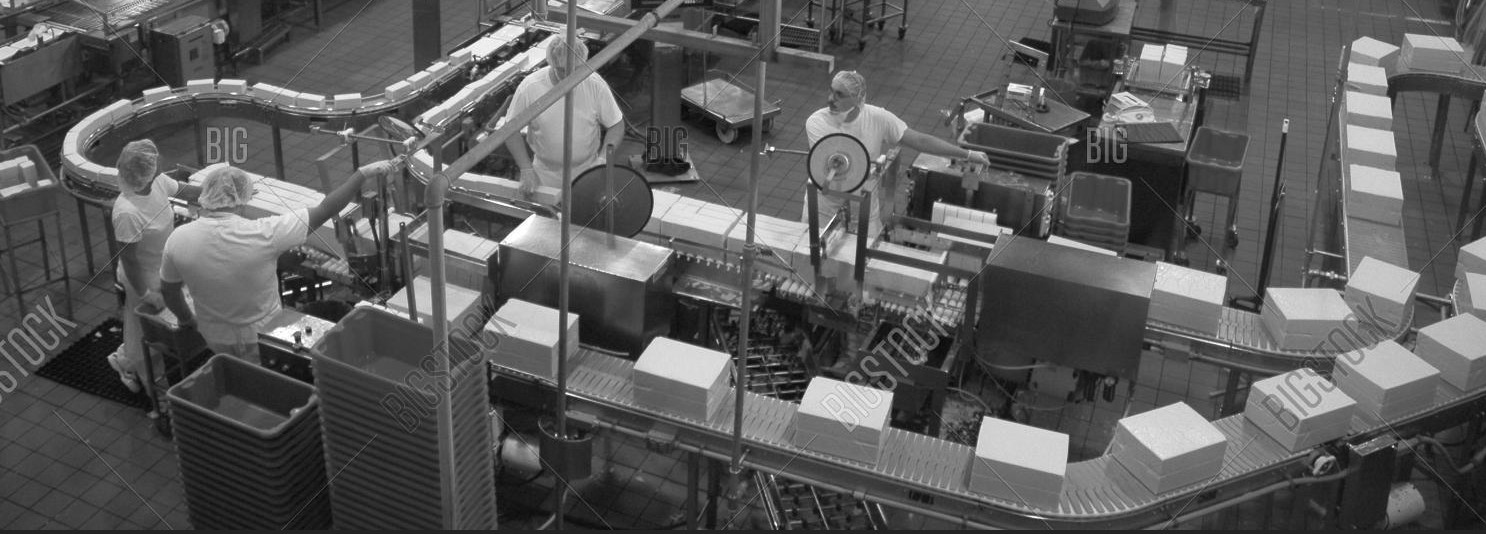

One way to boost productivity in traditional factories is to use assembly line.
From Wikipedia:
An assembly line is a manufacturing process (often called a progressive assembly) in which parts (usually interchangeable parts) are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from workstation to workstation where the parts are added in sequence until the final assembly is produced. By mechanically moving the parts to the assembly work and moving the semi-finished assembly from work station to work station, a finished product can be assembled faster and with less labor than by having workers carry parts to a stationary piece for assembly.
Let’s try to set it up in our toy car factory.
We can use go block from core.async to simulate a worker, and chan to simulate the conveyer belt.
Let’s draw our blueprint.
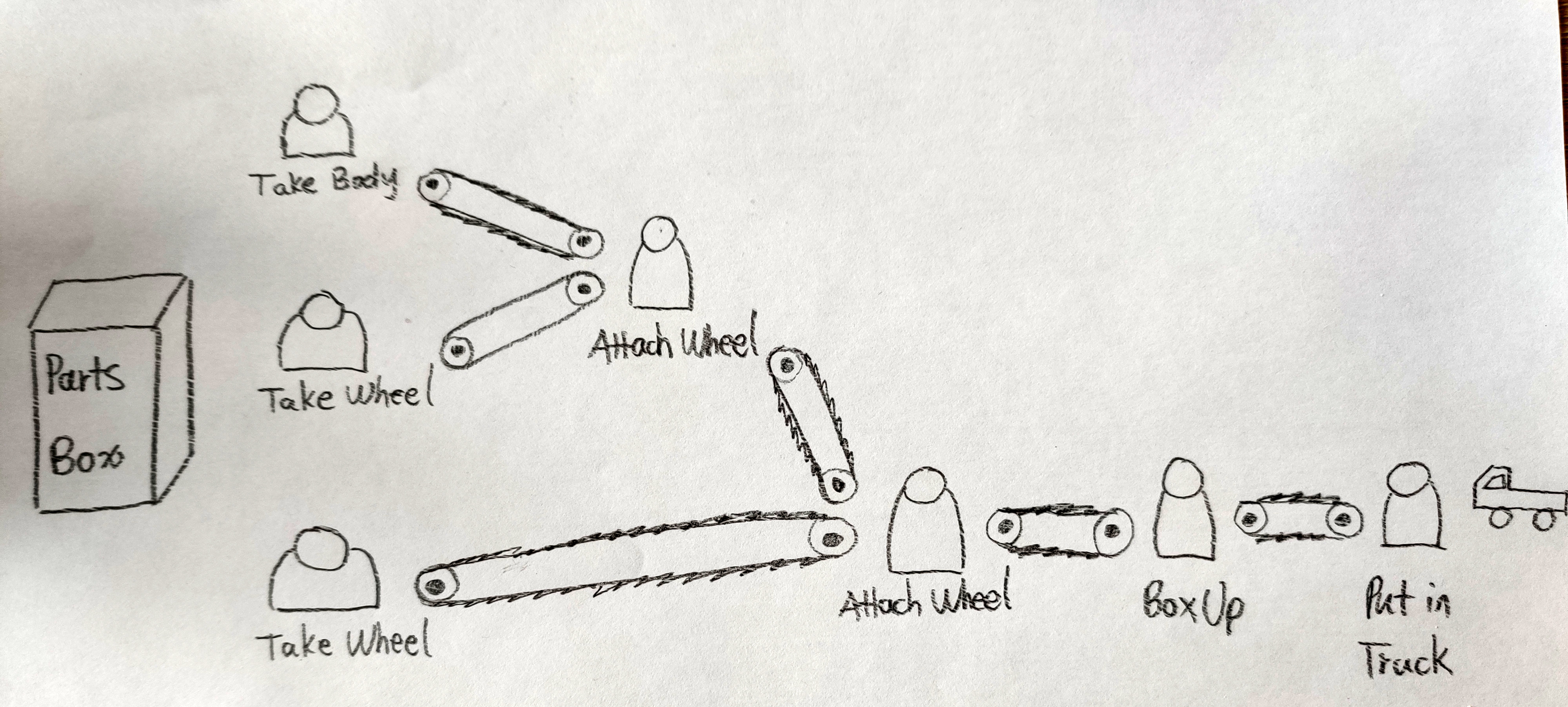
Then code it up.
(defn assembly-line []
(let [body-chan (chan)
wheel1-chan (chan)
wheel2-chan (chan)
body+wheel-chan (chan)
body+2-wheels-chan (chan)
box-chan (chan)]
(go
(while true
(let [body (loop []
(let [part (take-part)]
(if (body? part)
part
(recur))))]
(prn "Got body")
(>! body-chan body))))
(go
(while true
(let [wheel1 (loop []
(let [part (take-part)]
(if (wheel? part)
part
(recur))))]
(prn "Got first wheel")
(>! wheel1-chan wheel1))))
(go
(while true
(let [wheel2 (loop []
(let [part (take-part)]
(if (wheel? part)
part
(recur))))]
(prn "Got second wheel")
(>! wheel2-chan wheel2))))
(go
(while true
(let [body (<! body-chan)
wheel1 (<! wheel1-chan)
bw (attach-wheel body wheel1)]
(prn "Attached first wheel")
(>! body+wheel-chan bw))))
(go
(while true
(let [bw (<! body+wheel-chan)
wheel2 (<! wheel2-chan)
bww (attach-wheel bw wheel2)]
(prn "Attached second wheel")
(>! body+2-wheels-chan bww))))
(go
(while true
(let [box (box-up (<! body+2-wheels-chan))]
(prn "Boxed up car")
(>! box-chan box))))
(go
(time
(dotimes [x 10]
(time
(put-in-truck (<! box-chan)))
(prn "Done!"))))))This looks complicated! But it is really not. If you follow the blueprint step by step this is not hard to follow.
But we have used only 7 workers / go blocks, we have 10 to spend. Let’s add 1 worker each to the attach-wheel and box-up. Since others are blocking on the shared resources anyway.
;; ...
(dotimes [x 2]
(go
(while true
(let [body (<! body-chan)
wheel1 (<! wheel1-chan)
bw (attach-wheel body wheel1)]
(prn "Attached first wheel")
(>! body+wheel-chan bw)))))
(dotimes [x 2]
(go
(while true
(let [bw (<! body+wheel-chan)
wheel2 (<! wheel2-chan)
bww (attach-wheel bw wheel2)]
(prn "Attached second wheel")
(>! body+2-wheels-chan bww)))))
(dotimes [x 2]
(go
(while true
(let [box (box-up (<! body+2-wheels-chan))]
(prn "Boxed up car")
(>! box-chan box)))))
;;...
Twitter
Google+
Facebook
Reddit
LinkedIn
StumbleUpon
Email